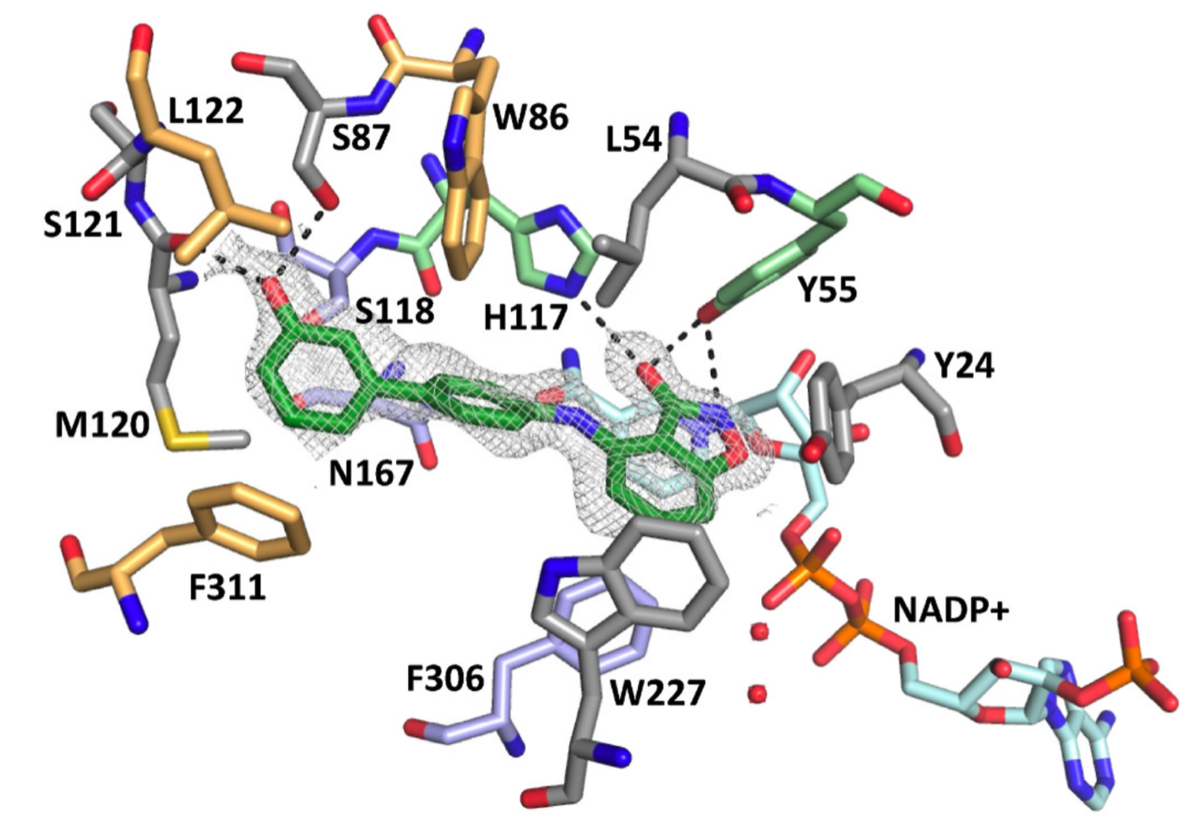
Targeting Aldo Keto Reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3)
Prostate Cancer (PC) is the most common diagnosed tumour affecting men. A fatal metastatic form is castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), caused by the reactivation of the androgen axis in androgen-deprived patients.
The enzyme AKR1C3 plays a central role in androgen biosynthesis in prostate tissue and is overexpressed in CRPC, therefore this enzyme has been investigated as an attractive therapeutic target for this disease.
Some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as flufenamic acid and indomethacin, are known to inhibit AKR1C3 in micromolar range, although unselectively toward the other isoforms, C1 and C2, as well as cyclooxygenases (COX). Starting from the structures of these drugs, we different bioisosteric replacement of the carboxylic acid function of NSAIDs to design new classes of AKR1C3 inhibitors, potent, selective towards the C3 isoform but above all devoid C1, C2 and COX activities.
Collaborations
- Prof. Simona Oliaro-Bosso, Biochemistry, Dep. of Drug Science and Technology, University of Torino (IT)
- Prof. Francesca Spyrakis, Molecular Modelling, Dep. of Drug Science and Technology, University of Torino (IT)
- Prof. Karla Frydenvang, Protein and Peptide Unit, Dep. of Drug Science and Pharmacology, University of Copenhagen (DK)
- Prof. Osman Asghar Mirza, Protein and Peptide Unit, Dep. of Drug Science and Pharmacology, University of Copenhagen (DK)
- Prof. Klaus Pors, Institute of Cancer Therapeutics, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Bradford (UK)
- Prof. Tomasz Wròbel, Department of Synthesis and Chemical Technology of Pharmaceutical Substances, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University of Lublin (PL)
- Prof. Amit Pandey, Biochemistry, University Children's Hospital Bern, University of Bern (CH)
- Dr. Caterina Peraldo-Neia, Laboratory of Cancer Genomics, Fondazione Edo ed Elvo Tempia, via Malta 3, 13900, Biella, Italy
- Dr. Ymera Pignochino, Candiolo Cancer Institute, FPO-IRCCS, Torino (IT)
- ATOMWISE, INC., 250 Sutter St., Suite 650, San Francisco, California (USA)
Representative pubblications
A.C. Pippione, C. Vigato, C. Tucciarello, S. Hussain, E. Salladini, H. H. Truong, Niel M Henriksen, G. Vanzetti, G. Giordano, D. Zonari, O. A. Mirza, K. Frydenvang, Y. Pignochino, S. Oliaro-Bosso, D. Boschi and M. L. Lolli. AI-based discovery of a new AKR1C3 inhibitor for anticancer applications. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00150
A.C. Pippione, S. Kovachka, C. Vigato, L. Bertarini, I. Mannella, S. Sainas, B. Rolando, E. Denasio, H. Piercy-Mycock , L. Romalho, E. Salladini, S. Adinolfi, D. Zonari, C. Peraldo-Neia, G. Chiorino, A. Passoni, O. A. Mirza , K. Frydenvang, K. Pors, M. L. Lolli, F. Spyrakis, S. Oliaro-Bosso,D. Boschi. Structure-guided optimization of 3-hydroxybenzoisoxazole derivatives as inhibitors of Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) to target prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 268, 116193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116193.
T. M Wrobel, K. Sharma, I. Mannella, S. Oliaro-Bosso, P. Nieckarz, T. Du Toit, C. D. Voegel, M. N. Rojas Velazquez, J. Yakubu, A. Matveeva, S. Therkelsen, F. Steen Jorgensen, A. V. Pandey, A. C. Pippione, M. L. Lolli, D. Boschi, F. Bjorkling. Exploring the Potential of Sulfur Moieties in Compounds Inhibiting Steroidogenesis. Biomolecules. 2023, 13(9), 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13091349
A.C. Pippione, Z. Kilic-Kurt, S. Kovachka, S. Sainas, B. Rolando, E. Denasio, K. Pors, S. Adinolfi, D. Zonari, R. Bagnati, M.L. Lolli, F. Spyrakis, S. Oliaro-Bosso, D. Boschi. New aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) inhibitors based on the hydroxytriazole scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 237, 114366. DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114366
Lolli, M.L., Carnovale, I.M., Pippione, A.C., Wahlgren, W.Y., Bonanni, D., Marini, E., Zonari, D., Gallicchio, M., Boscaro, V., Goyal, P., Friemann, R., Rolando, B., Bagnati, R., Adinolfi, S., Oliaro-Bosso, S., Boschi, D.Bioisosteres of Indomethacin as Inhibitors of Aldo-Keto Reductase 1C3 . ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10 (4), 437-443 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00484
A.C. Pippione, , I. M. Carnovale, D. Bonanni, M. Sini, P. Goyal, E. Marini, , K. Pors, S. Adinolfi, , D. Zonari, C. Festuccia, W. Y. Wahlgren, R. Friemann, R. Bagnati, D. Boschi, S. Oliaro-Bosso, and M. L. Lolli Potent and selective aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) inhibitors based on the benzoisoxazole moiety: Application of a bioisosteric scaffold hopping approach to flufenamic acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 930-945 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.040
A. C. Pippione, A. Giraudo, D. Bonanni, I. M. Carnovale, E. Marini, C. Cena, A. Costale, D. Zonari, K. Pors, M. Sadiq, D. Boschi, S. Oliaro-Bosso* and M. L. Lolli.* Hydroxytriazole derivatives as potent and selective aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) inhibitors discovered by bioisosteric scaffold hopping approach. Eu. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 936-946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.046